MySQL
准备
在开始之前,我们需要在本地安装并运行 GreptimeDB 和 Grafana。
- GreptimeDB 用于存储和查询数据。
- Grafana 用于可视化数据。
这里我们使用 Docker Compose 来启动 GreptimeDB 和 Grafana。为此,创建一个 docker-compose.yml 文件,内容如下:
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana-oss:9.5.15
container_name: grafana
ports:
- 3000:3000
greptime:
image: greptime/greptimedb:latest
container_name: greptimedb
ports:
- 4000:4000
- 4001:4001
- 4002:4002
- 4003:4003
- 4004:4004
- 4242:4242
command: "standalone start --http-addr 0.0.0.0:4000 --rpc-addr 0.0.0.0:4001 --mysql-addr 0.0.0.0:4002 --postgres-addr 0.0.0.0:4003 --opentsdb-addr 0.0.0.0:4242"
volumes:
- ./greptimedb:/tmp/greptimedb
networks: {}
然后执行以下命令:
docker-compose up
接下来的步骤假设你按照上面的文档安装了 GreptimeDB 和 Grafana。
尝试基本的 SQL 操作
连接
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 4002
你同样可以使用 PostgreSQL 连接到数据库
psql -h 127.0.0.1 -p 4003 -d public
建表
注意: GreptimeDB 提供了一种 schemaless 的数据写入方法,不用像使用其他协议那样手动创建表。详情请参见 自动生成表结构。
现在我们通过 MySQL 创建一个表。先创建 system_metrics 表,其中包含系统资源指标,包括 CPU /内存/磁盘的使用,这些数据每 5 秒就会被抓取一次。
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS system_metrics (
host STRING,
idc STRING,
cpu_util DOUBLE,
memory_util DOUBLE,
disk_util DOUBLE,
ts TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY(host, idc),
TIME INDEX(ts)
);
Field 描述:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| host | string | The hostname |
| idc | string | The idc name where the host belongs to |
| cpu_util | double | The percent use of CPU |
| memory_util | double | The percent use of memory |
| disk_util | double | The percent use of disks |
| ts | timestamp | Timestamp column incrementing |
- 如果用户使用其他协议,该表可以自动创建。请参考 Create Table。
- 关于创建表的 SQL 信息,请参考 CREATE。
- 关于数据类型,请参考数据类型。
数据写入
使用 INSERT 语句是向表添加数据的一个简单方法。通过下面的语句,我们向 system_metrics 表插入了九条记录。
INSERT INTO system_metrics
VALUES
("host1", "idc_a", 11.8, 10.3, 10.3, 1667446797450),
("host1", "idc_a", 80.1, 70.3, 90.0, 1667446797550),
("host1", "idc_b", 50.0, 66.7, 40.6, 1667446797650),
("host1", "idc_b", 51.0, 66.5, 39.6, 1667446797750),
("host1", "idc_b", 52.0, 66.9, 70.6, 1667446797850),
("host1", "idc_b", 53.0, 63.0, 50.6, 1667446797950),
("host1", "idc_b", 78.0, 66.7, 20.6, 1667446798050),
("host1", "idc_b", 68.0, 63.9, 50.6, 1667446798150),
("host1", "idc_b", 90.0, 39.9, 60.6, 1667446798250);
关于 INSERT 语句的更多信息,请参考 INSERT。
数据查询
想要从 system_metrics 表中选择数据,可以使用 SELECT 语句:
SELECT * FROM system_metrics;
查询结果如下:
+-------+-------+----------+-------------+-----------+---------------------+
| host | idc | cpu_util | memory_util | disk_util | ts |
+-------+-------+----------+-------------+-----------+---------------------+
| host1 | idc_a | 11.8 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_a | 80.1 | 70.3 | 90 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_b | 50 | 66.7 | 40.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_b | 51 | 66.5 | 39.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_b | 52 | 66.9 | 70.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_b | 53 | 63 | 50.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:57 |
| host1 | idc_b | 78 | 66.7 | 20.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:58 |
| host1 | idc_b | 68 | 63.9 | 50.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:58 |
| host1 | idc_b | 90 | 39.9 | 60.6 | 2022-11-03 03:39:58 |
+-------+-------+----------+-------------+-----------+---------------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
用户可以使用 count() 函数获取表格中所有行的数量:
SELECT count(*) FROM system_metrics;
+-----------------+
| COUNT(UInt8(1)) |
+-----------------+
| 9 |
+-----------------+
avg() 函数返回特定字段的平均值:
SELECT avg(cpu_util) FROM system_metrics;
+------------------------------+
| AVG(system_metrics.cpu_util) |
+------------------------------+
| 59.32222222222222 |
+------------------------------+
使用 GROUP BY 子句,将具有相同数值的行分组为汇总行。例如按 idc 分组的平均内存使用量:
SELECT idc, avg(memory_util) FROM system_metrics GROUP BY idc;
+-------+---------------------------------+
| idc | AVG(system_metrics.memory_util) |
+-------+---------------------------------+
| idc_a | 40.3 |
| idc_b | 61.942857142857136 |
+-------+---------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.03 sec)
关于 SELECT 语句的更多信息,请查看 SELECT 文档。
采集主机指标
为了通过 MySQL 快速开始,我们可以使用 Bash 脚本收集系统指标,例如 CPU 和内存使用情况,并通过 MySQL CLI 将数据发送到 GreptimeCloud。 源代码位于 GitHub.
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GreptimeCloudStarters/quick-start-mysql/main/quick-start.sh | bash -s -- -h 127.0.0.1 -d public -s DISABLED -P 4002
数据可视化
GreptimeDB 控制台
GreptimeDB 提供了用户友好的控制台帮助用户探索数据。
当 GreptimeDB 按照上文的准备环节启动后,你可以通过 URL http://localhost:4000/dashboard 访问控制台。
将 SQL 写入命令文本,然后单击 RUN ALL,就能获取 system_metrics 中的所有数据。
SELECT * FROM system_metrics;
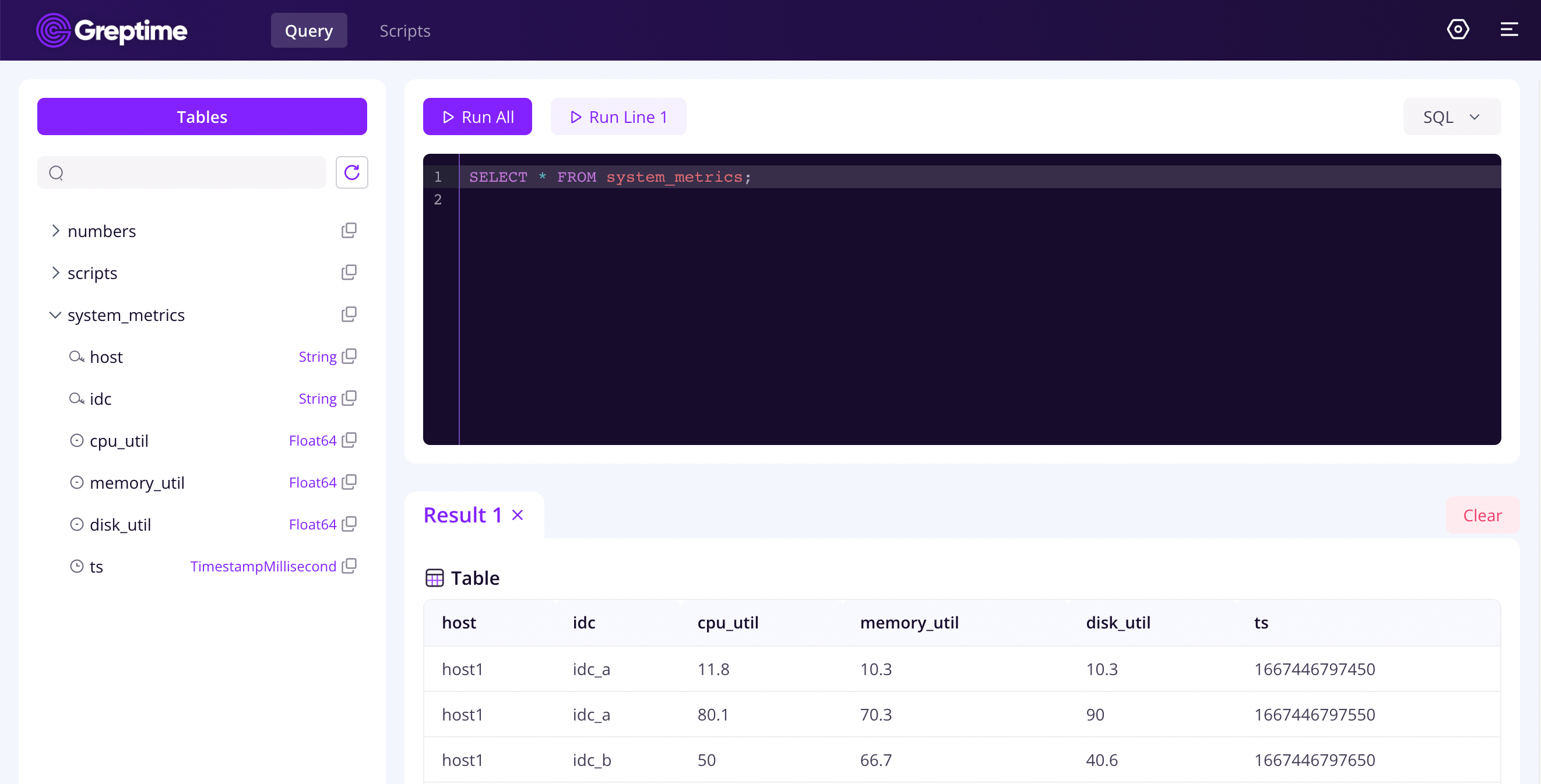
Grafana
添加数据源
你可以通过 http://localhost:3000 访问到 Grafana,并使用 admin 作为用户名和密码登录。
GreptimeDB 可以作为 MySQL 数据源配置在 Grafana 中。
点击 Add data source 按钮,选择 MySQL 作为类型。
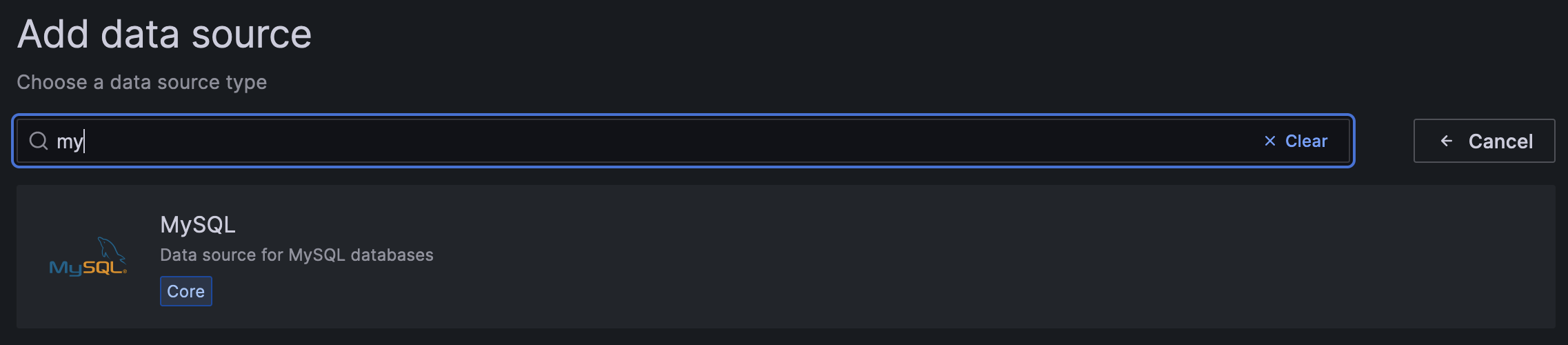
填写以下信息:
- Name:
GreptimeDB - Host:
greptimedb:4002. The hostgreptimedbis the name of GreptimeDB container - Database:
public - SessionTimezone:
UTC
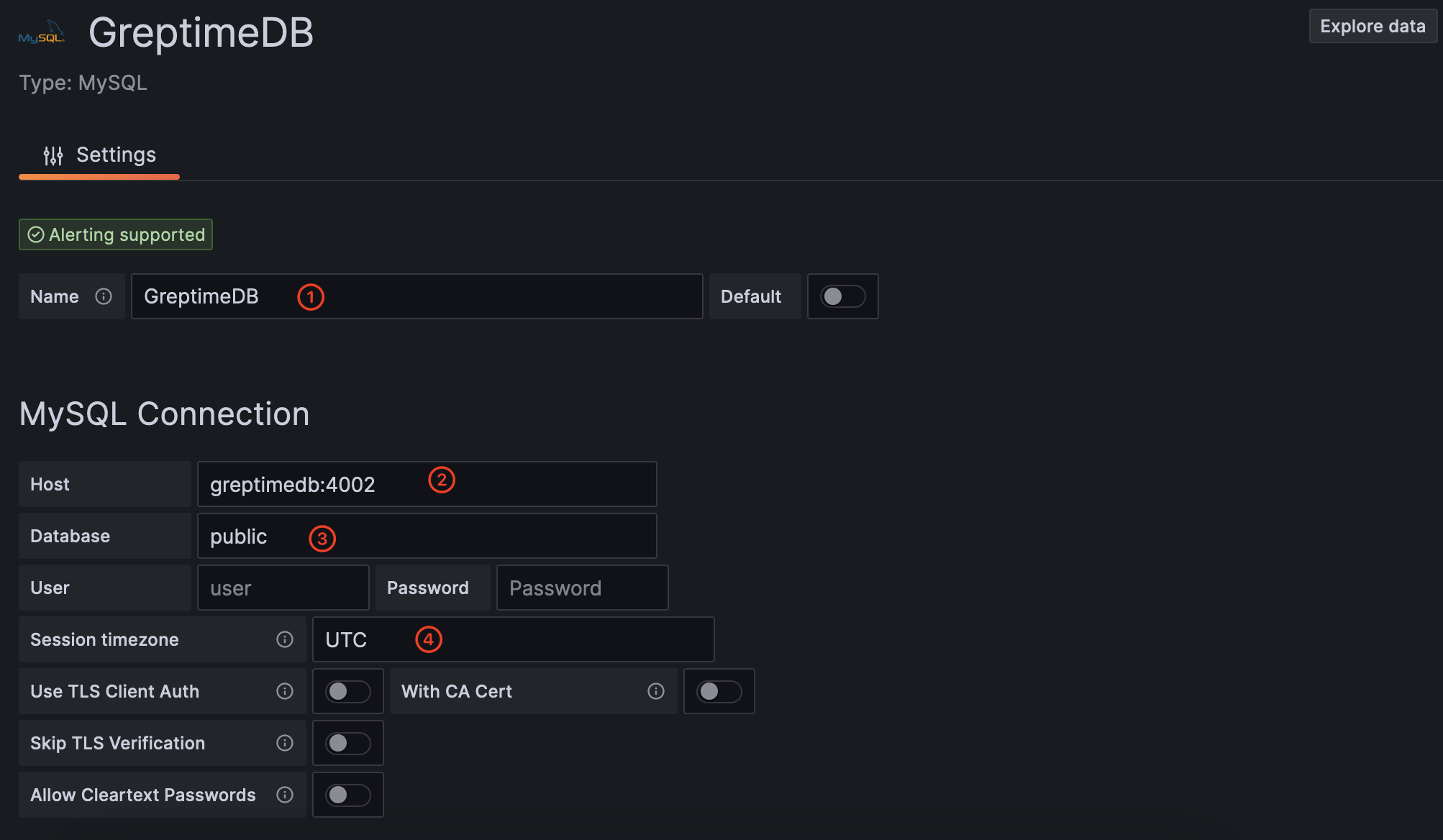
点击 Save & Test 按钮,确保数据源配置成功。
有关使用 MySQL 作为 GreptimeDB 数据源的更多信息,请参考 Grafana-MySQL。
创建仪表盘
在 Grafana 中创建一个新的仪表盘,点击 Create your first dashboard 按钮。
然后,点击 Add visualization,选择 GreptimeDB 作为数据源。
在 Query 标签页中,确保你选择了 GreptimeDB 作为数据源,接下来选择 Time series 作为格式,
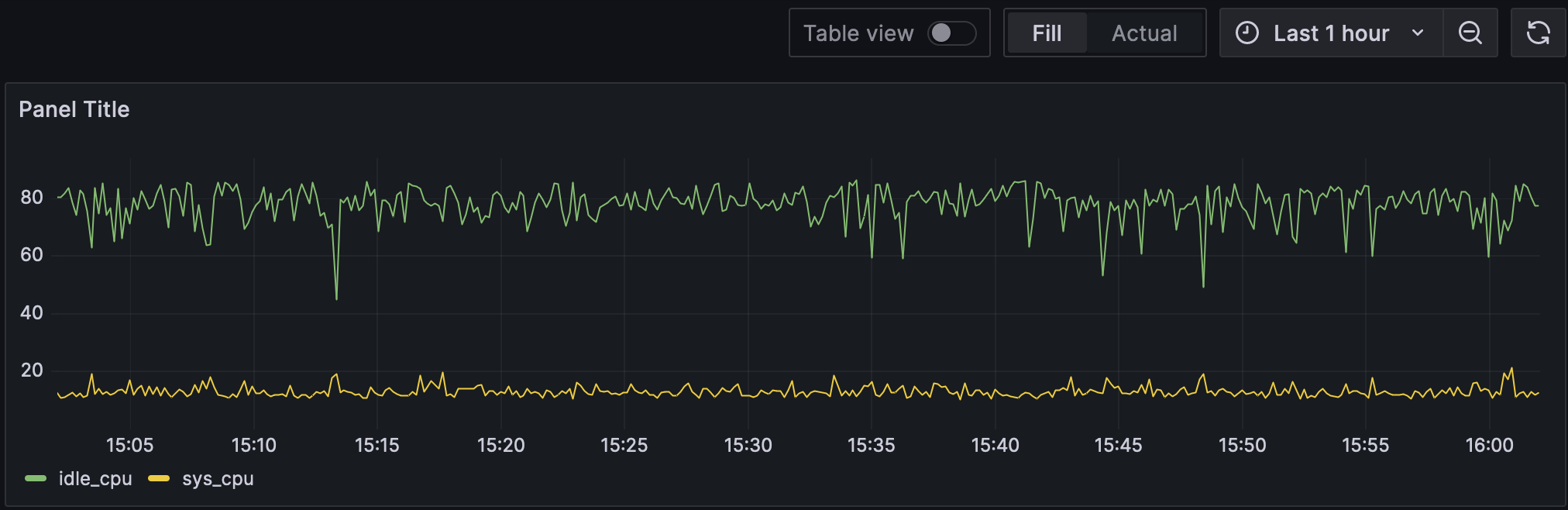
切换到 Code 标签页,写入以下 SQL 语句。注意我们使用了 ts 列作为时间列。
SELECT ts AS "time", idle_cpu, sys_cpu FROM public.monitor
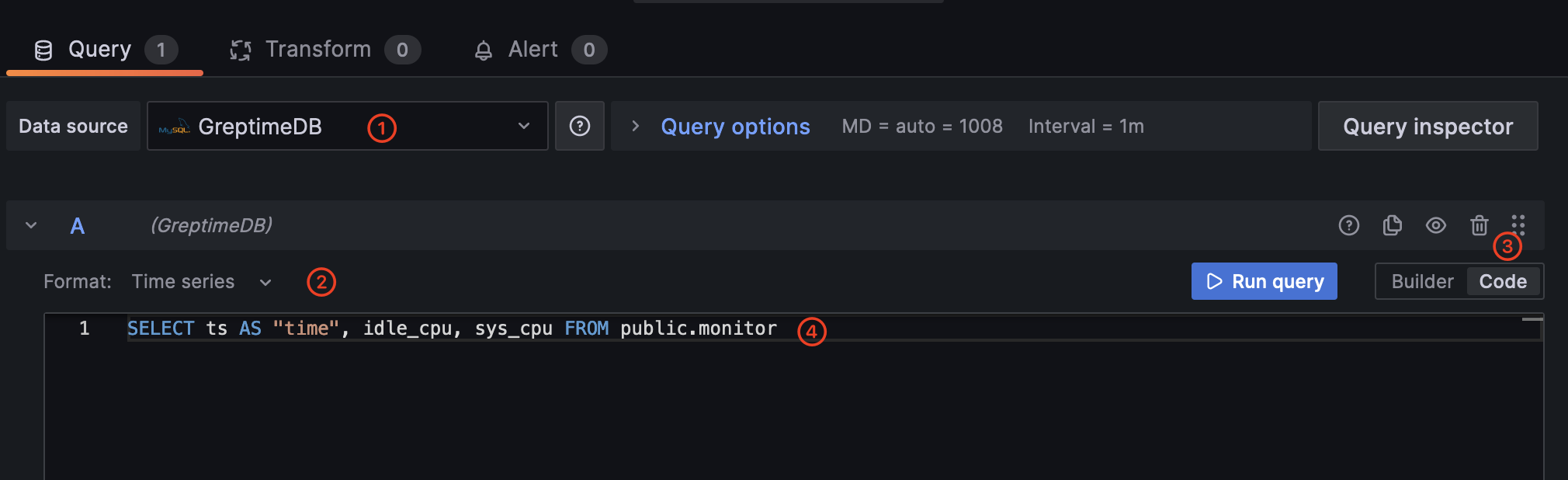
点击 Run query 查看指标数据。
下一步
恭喜你已经快速体验了 GreptimeDB 的基础功能! 现在,你可以通过访问 用户指南文档 来探索更多 GreptimeDB 的功能。